Weather Routing Pi
Author: Sean D’Epagnier
Maintainers: Rick Gleason, Jon Gough and the Plugin Team
PI Manager Workflow: Testplugin
Purpose of Weather Routing (WR)
Luckygrib has superb introductory documentation for WeatherRouting. This started out as an excellent grib viewer/download for ipad and imac only. This documentation is worth reviewing first for general principals.
Create optimized Weather Routes based on:
-
Grib_pi plugin using downloaded predictive grib files (grb, grb2) with wind, wave & current data
-
Climatology_pi plugin using built in NOAA 30 year data, averaged by month with wind, wave and current data
-
GSHHS High Resolution Background It is easiest and best to install GSHHS using the Options > Chart > Chartdownloader. Required to improve routing with “Detect Land” checked.
-
Your Boat’s Performance Data - Starting sources VPP Calculated Polars or Measurement in various conditions (see below)
Boat Performance Data - Polar Data
The plugin also requires Boat performance data (polar data). There are many Polar Data files built in and included as a part of the plugin. Also Polar Data can be developed from:
-
Boat Instrument data created while sailing in non-current conditions. See
-
VDRplayer Manualjavascript:%20indexmenu_18973814515a5cc87ac6b23.o(80);
-
VPP Velocity Prediction Programs using physical measurements of the boat.
-
Additionally there are many Polar Data files available in the Weather_routing Plugin.
-
You may find a starter polar file for your boat (EG: C:\Program Files(x86)\OpenCPN 4.8.0\plugins\weather_routing_pi\data\polars)
Note: Boat performance data should be in a format compatible with weather_routing_pi. The plugin will convert the file to a format it can use (fixing certain minor variations and irregularities) or declare it unusable.
Note: Grib data is predictive data, and as such it will be subject to change. Generally data past 3-4 days it is unreliable, and the longest grib available is 16 days (with a larger time interval between data points). For longer voyages, Climatology_pi data can be used as an alternative data source to extend the routing calculations.
Boat Performance Data - Outside Sources
-
Weather_Routing_pi has a full set of polar files, but there are other sources.
-
Distant Shores on Polar Performance Good advice, adjust VPP Polars for Cruising
-
Boat Performance Data. Record in consistent conditions for various conditions, see why.
What is Weather Routing useful for?
-
Trip or voyage planning.
-
Determining good weather windows for starting the trip.
-
Calculate multiple routes at the same time.
-
Highlight and step through multiple “completed' routes at the same time.
-
Approximation of better routes dependent on goals and constraints set.
-
Adjust the Wind Speed as a percentage, which helps to set realistic goals.
-
Avoidance of predicted high winds (hurricanes & typhoons), areas of light winds, large waves, etc.
-
Show possible sail changes and % crossover.
-
Summary metro chart of the voyage that shows the weather visually.
-
Number of tacks, % upwind/downwind, etc. to determine how difficult the voyage will be.
-
Estimate trip total time, distance, average speed to help determine the stores needed.
-
Useful for crew members planning airline tickets, but only as a rough estimate.
-
Remember that it is only as good as predictive and average data!
What does Weather Routing look like?
Weather Routing: Calculation of the fastest/safest route from a starting point to an ending point given the current national weather forecasts, available wind data, current oceanic currents , the performance of your vessel, and comfort criteria (storms, wind, waves, etc.) More about Optimum Weather Route
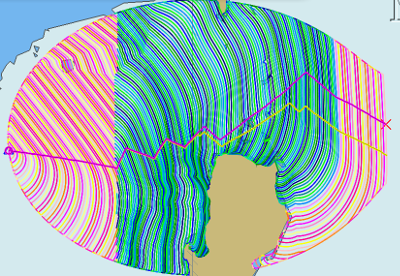
When the weather route is displayed, Grib and Climatology calculations use different color schemes. as in the route above.
Wind Data Sources - Grib and Climatology
-
Isochrones While calculating a Weather Routing the plugin will calculate the location of the boat for a given time interval (eg: 1 hr, 4hr, 6 hr or 12hr ) and display an isochrone contour line which represents how far the boat will sail in a given direction, based on the weather and boat conditions, for each successive time interval. Isochrones are like contour lines around the starting point. Think of Isochrones as showing an intermediate destination time lines with different distances from the start point.
-
Left Pink-Yellow Isochrones: Beginning passage uses Climatology data because the boat is outside the Grib area.
-
Middle Blue-Cyan Isochrones: Computation is based on Grib data.
-
Right Pink-Yellow Isochrones: End of passage, Grib data not available so again Climatology data is used.
-
If the transition from grib to climatology is not uniform, then the climatology data is not as reliable in that situation.
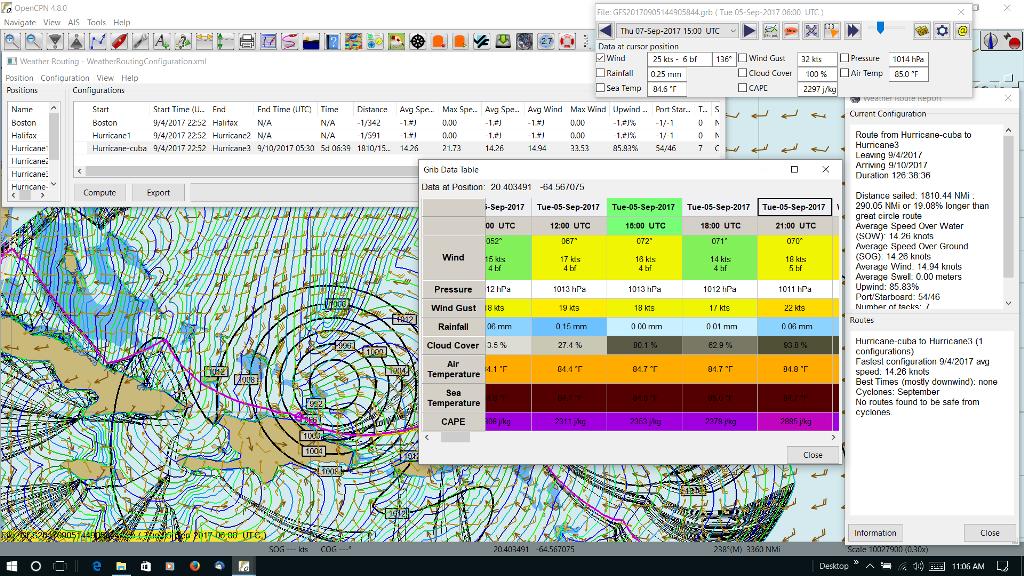
Cuba to Puerto Rico,title="Irma Cuba to Puerto Rico"]]
Example: Routing from Cuba to Puerto Rico through Hurricane Irma.(Don’t ever do this!) Showing Grib_pi “Weather Data” (Right Click on Chart) and Weather_routing View > Report & View > Plot.
Terminology and Route Icons
-
Route or Optimal Route: Thick magenta line from the start “triangle” to the finish “X”.
-
Cursor Route: Thin yellow line that follows the cursor around. This is the optimal route to the cursor.
-
Triangle: Start point defined by the “Weather Routing Position” selected in the “Configuration”.
-
X: End point defined by the “Weather Routing Position” selected in the “Configuration”.
-
Square: Small squares along the route, are sail/polar file changes [Not shown].
-
Circle on the route is the calculated Boat location for that time frame.
-
Configuration and Computation of a routing is at the center of the plugin.
-
Configuration Defaults Options and Constraints you may need for reference.
-
Configuration Terminology Definitions available from within the Plugin, Help > Information Menu. Reference Common Terms used in this Manual.
-
-
Also look at the next screenshot below for examples.
Techniques and Tools
-
Configuration Terminology Definitions available from within the Plugin, Help > Information Menu. Review this carefully while stepping through the plugin menus, looking particularly at Edit Boat.xml and Edit Polar File (.csv, .txt, .pol) Understand the menu system here and how it works. Boat.xml simply contains a list of boat polar files to use in the routing. The polar files can be edited, saved and saved as.
Weather Routing is a deep plugin which can use three other plugins concurrently, so stick to basics when starting out.
-
Grib Step Through Step through the Grib file changing time, frame by frame, hour by hour, to understand the Routing better.
-
Data at Cursor: Run your cursor along the route with the Grib_pi Menu and “Wind speed at Cursor” on. It is very useful for diagnostics along a problematic route.
-
Grib Weather Table: When a grib shows on the screen, right click and pick “Weather Table” (see screenshot below)
-
WeatherRouting additional information After computation of a routing, highlight the Configuration, pick View in the menu at the top then select Settings, Statistics, Report, Plot or Cursor for more information. (See screenshot below for examples)
-
WeatherRouting settings Pick View > Settings.
Summary
-
Use the Grib Plugin and recently downloaded grib files for completing grib predictive routing (1-8 days).
-
Use the Climatology Plugin to find and plan long term cruising routes, (most useful in prevailing winds areas).
-
Use both Grib and Climatology data, to allow the routing to be extended past the time/date range of the grib file, which uses Climatology data to extend the Routing based on NOAA “average” or “most likely” data.
-
Use both Grib and Climatology to use “tidal current data” if the grib does not contain it, or to use climatology to avoid areas ofcyclones.
-
Your first goal should be to read this manual several times while trying to understand the menus and structure. Then to make a routing yourself. The “Configuration” and “Computation” of an optimal weather routing is at the heart of this plugin.
Cleanup of Prior Installation
Generally we recommend that the plugin and configuration artifacts should be completely removed before installation of the new version, in order to allow the intended initialization files to be copied from the System files ProgramFiles (x86) folders to User Files ProgramData. The plugin expects a clean environment before initializing and copying the appropriate files into the user directories. You must “Clean” your opencpn files of all weather_routing files and folders or the initialization that is required will not occur. For windows users, from:
-
C:\Program Files (x86)\OpenCPN 4.8.0 —> Run Uninstall Weather_routing.exe as administrator.
-
C:\ProgramData\opencpn —> Open opencpn.ini in Notepad++ and remove all lines for weather_routing and weatherrouting, including the order of plugins “weatherrouting” reference.
-
C:\ProgramData\opencpn\plugins —> Remove the Weather_routing directory.
Download and Installation
Make sure you choose the file that is compatible with your computer system.
In this manual we presume it’s Windows, so we choose the Windows
setup-package.
We assume you know where to find the files you download from the Internet (if you don’t: quit now and read the manual of your computer before doing anything else with it
Double-click the downloaded file (with “weather_routing_pi” in the name and ”.exe“ as extension) and follow the set-up instructions. If you are doing parallel installs of OpenCPN make sure the plugin goes into the proper version of OpenCPN!
That’s it. But before you can actually use Weather_Routing_pi, you first have to Enable the plug-in in OpenCPN.
Grib_pi plugin is included with OpenCPN, but you will need to install Climatology_pi plugin if you wish to use that type of data.
Enable OpenGL
You need to activate OpenGL in order to have the route display on top of the grib layer!
Standard Actions
Goal
Weather_routing is remarkably flexible, but with that comes complexity. New users must not dive in changing settings without understanding what they are doing or how it affects “Computation”.
-
Generally the “Reset” settings are the most reliable settings available and after hitting “Reset” most of the settings can be left alone.
-
However there are definitely some settings the user must set manually in order to get any results! The goal here is to make your first routing compute properly and “Complete”.
Please follow this tutorial carefully and you will succeed the first time. Once you get familiar with the interface and have had successes, learn all the features gradually, changing and adjusting one setting at a time.
1.Setup Grib_pi Data
Grib_pi is installed with OpenCPN. Learn how to use it and download a fresh Grib file with wind, current & waves.
-
Initially the grib area should be larger than the area between start and finish by at least two time intervals,
-
Should be for more days than expected (refine this later).
-
Set the grib at the starting time and then move it one or two time intervals forward, later with more experience you may set the Grib data and time at what you want.
2. Setup Climatology_pi Data
Climatology_pi should be installed as directed.
-
Enable Climatology_pi. Learn how to use it.
-
When Climatology_pi is Enabled under Options > Plugins , the “Weather_routing Configuration” - Data Source - Climatology Dropdown Menu (Disable, Cumulative Map, Cumulative Calms, Most Likely,Average) will become accessible for selection.
-
The Weather_Routing Plugin will access Climatology data automatically once these settings are selected.
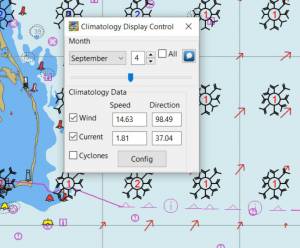
Climatology NOAA 30 year average Wind and Current data in September near Cape Lookout
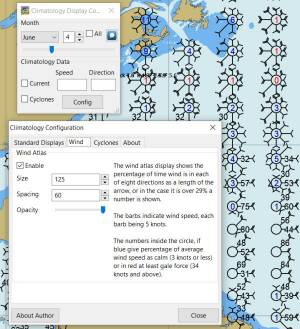
Climatology Configuration of Wind Roses (Size=100 and Spacing=50 is good
too.)
3. Install GSHHS High Resolution Background
Download and install to improve routing with “Detect Land” checked.
If you are working with Land Interface a lot, this is not optional! Best to install it.
4. Weather Routing Setup
Four Transatlantic Configurations that will Compute using Climatology Wind Data
Confirm that the Weather_Routing Plugin has been installed.
*Files & Pathnames*
It is important that you use this configuration for Windows (Linux use comparable User accessible directories):
-
Main Path for support files: C:\ProgramData\opencpn\plugins\weather_routing
-
WeatherRoutingConfiguration.xml: C:\ProgramData\opencpn\plugins\weather_routing
-
Polar Files (.pol,.txt,.csv): C:\ProgramData\opencpn\plugins\weather_routing\polars
-
Boat.Xml Files: C:\ProgramData\opencpn\plugins\weather_routing\boat
(Note the weather_routing installation may not create these files in the correct location, and may put them under C:\Program Files (x86)\opencpn\plugins\weather_routing/data. If this is the case, just download the Weather Routing Setup files below and install as shown above.
Weather Route setup for MacOS and for inclusion in the Weather Routing wiki.
Run some Weather Routing Routes
-
Start Climatology_pi, although it will start automatically if called.
-
Start Grib_pi (normally used, but not necessary with the default “Configurations” which use Climatology.
-
Set the Grib Date has been already set in the default configurations.
-
Then open Weather_routing_pi.
-
Confirm the “Boat section” path is correct as shown above in the Pathname list.
-
Confirm the “Polar” path is correct as shown above in the Pathname list.
-
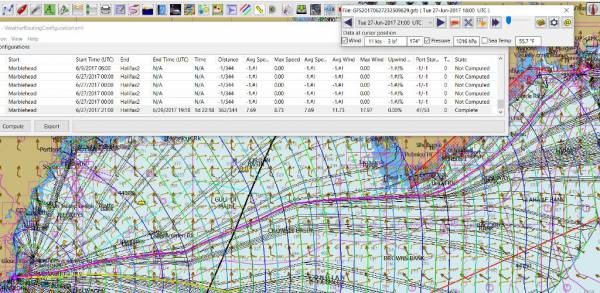
In the menu you should find 5 configurations for transatlantic routes.
-
Pick a route and then select “Compute from the bottom of the menu.
-
Check that the isobars and route is drawn.
-
Try “Computing” the other routes, noticing how the settings have been changed, and what files are being used.
-
Once you are pretty confident about this, go to the next step, which is to create your own configurations.
5. WR Not a substitute for sound judgment & realistic goals
You must Configure weather_routing to match your sound judgment and realistic goals. You are in control, use your own judgement when you review the results. This cannot be emphasized enough. Weather_Routing_pi is just a tool in your hands, you are in control.
6. WeatherRoutingConfiguration.XML Menu
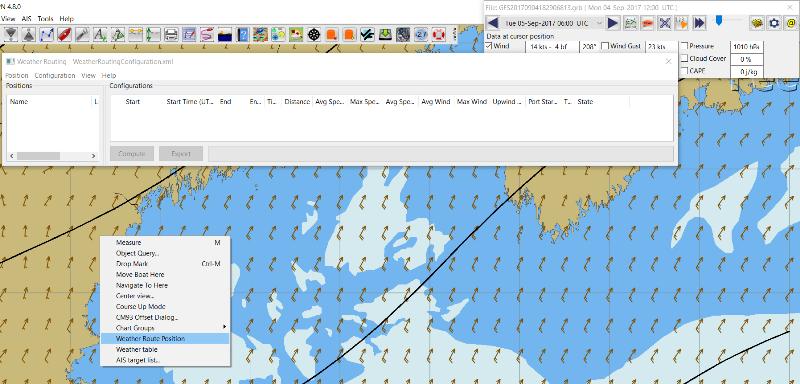
If the plugin is downloaded and installed, with default settings unchanged (or “Reset All” is used), the plugin should create an optimized weather routing with just a few specific additional settings and “computation”.
-
Complete Setup Grib_pi Data and Setup Climatology_pi Data as described above.
-
Start by clicking on the Toolbar Weather_routing plugin Icon to open the Weather_routing_Configuration Menu.
-
WR WeatherRoutingConfiguration.xml Menu

-
Define two Weather Route Positions on the chart within the “grib area”. Hover the mouse at a selected location, Right Click, and then pick “Weather Route Position” from the popup menu. Make a “Boston” and a “Halifax” Weather Route Position.
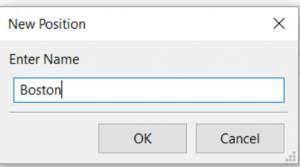
-
In the WR WeatherRoutingConfiguration.xml menu select ConfigurationNew. The Weather Routing Configuration Menu will appear with “Start”=Boston and “End”=Halifax.
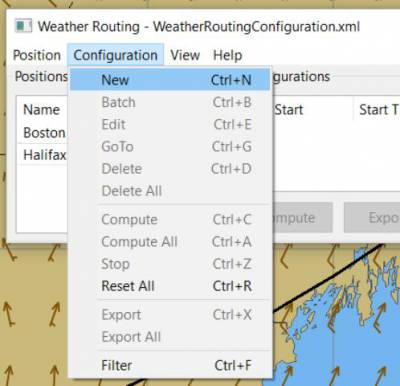
7. Weather Routing Configuration Menu
-
Scan the setting to check that they are as shown in the image.
-
Check Start and End selections. If not correct, select these WP Positions from the respective dropdowns.
-
Set Start Date & Time. If you have set start date & time in Grib_pi as described above.
-
From the Weather Routing Configuration Menu click Grib Time to set the Start Date/Time used by the “Configuration” for the routing. The Grib Time used will be the current frame used and visible in Grib_pi. There are other ways to do this, but use this way to start.
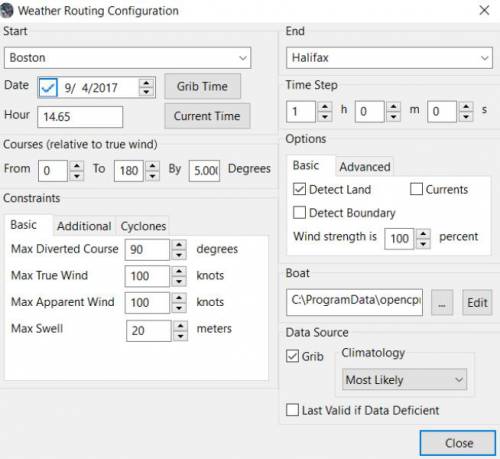
8. WR Configuration > Boat.xml Menu - Edit
Weather_routing_pi uses [Boat].xml files to store multiple [Polar].pol, *.csv or *.txt filenames which are used with the Current ”Configuration”. Also the [Boat].xml file can be “Save as Boat” to another boat filename such as Boat-Test.xml or [Your-Boat-Medium-Wind-Heavy-Sea-Clean-Bottom].xml.
Many new users have have trouble “Completing” Weather Route Configurations due to Polar:Fail messages, which is often because the single polar they have used only has TWS from 6-20 knots and does not span the entire true wind speed range of the particular grib file being used.
To help new users when starting out, we will create a Boat-test.xml file that references three “polar-xx-xxx-x-xx.pol” files which cover a full TWS (True Wind Speed) range of 0-60 knots. The Weather_routing Configuration will utilize the best polar information from the multiple polar files in Boat-test.xml after computing the “Sail/Polar Crossover” calculations between the different polar files being used.
unzip to C:\ProgramData\opencpn\plugins\weather_routing\boat which are preconfigured files that should work with the Polar and WeatherRoutingConfiguration.XML file downloads. These files are the same as Weather_Routing_Setup above.
-
Boat.XML
-
Boat-test.XML
-
Boat-Test-Power.XML
Later on, after some successful weather routings, users are encouraged to create separate boat performance [polar].pol files for:
-
Sets of Sails Used (Sail Changes, First & Second Reefs)
-
Sea conditions (Waves - Rough, Chop, Height, Period)
-
Boat load (Race Light, Cruising, Heavy)
-
Boat bottom condition (Smooth, Grass, Barnacles, Loaded)
Example of useful Polars for your boat:
-
LW-light wind (0-5 knots) Sail set #1
-
MW-medium wind (5-18 knots) Sail set #2
-
HW-heavy wind (18-24 knots) Sail set #3
-
SW-storm wind (24-32 knots) Sail set #4
-
GW-gail wind (32-60 knots) Hove to, Drogue.
-
LW-lightwind-Power (0-3 knots) Polluting Internal Combustion Engine
Using the sails normally used for each type of wind, such that the full range of True Wind Speed (TWS) is represented (0-60 knots).
|
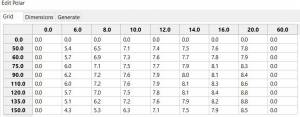
These files can be inspected and edited with a text editor such as
Notepad++ or they can more easily be edited using the Polar section
Edit Menu and the two Tabs Grid and Dimensions. Learn how they are
formatted (particularly .pol) as this will assist you in creating
useful polars for your boat. *Polar Files for Learning (User Friendly) |
Please Download, unzip and copy the six .pol files listed below into your data\polars directory. For Windows use: C:\ProgramData\opencpn\plugins\weather_routing\data\polars These files are the same as *https://opencpn.org/wiki/dokuwiki/doku.php?id=opencpn:opencpn_user_manual:toolbar_buttons:plugins:weather:weather_routing#weather_routing_setup[Weather_Routing_Setup] above.
Three Stepped Range TWS Files used together (use either Sail or Power for TWS-0-6)
-
TWS-0-6-Power.pol (power for light winds)
-
TWS-0-6.pol (sail)
-
TWS-0-20.pol
-
TWS-20-60.pol
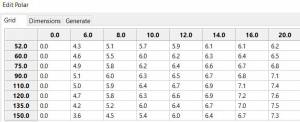
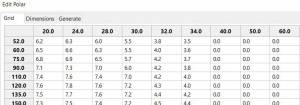
Single File with Full Range TWS 0-60 knots
-
Test-TWS-0-20+60.pol
[Boat].xml files are normally located here for Windows: C:\ProgramData\opencpn\plugins\weather_routing
In Boat.xml Menu Edit please Add these files
-
TWS-0-6-Power.pol (use power in light winds)
-
TWS-0-20.pol
-
TWS-20-60.pol
Use of these three files will cover a wide wind range from 0-60 knots (with 0-6 under power). If you just want to use one file for TWS 0-60 knots use Test-TWS-0-20+60.pol.
Once the three files have been added, next pick Save as Boat then type Boat-Test and “Save” to create and save “Boat-Test.xml”
Now when Computing “new” Configurations first check the configuration by selecting Boat-Test.xml at the Boat section “….” just ahead of “Edit” in the “Configuration” Menu. Once that completes properly, then create a “Boat.xml” file for your boat with reference to your normal boat polars and use that.
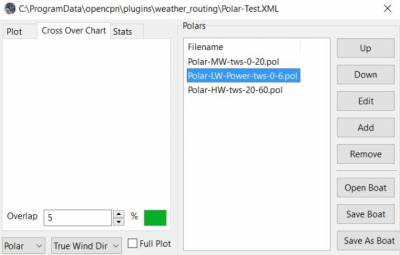
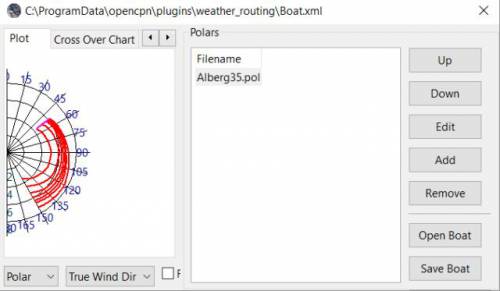
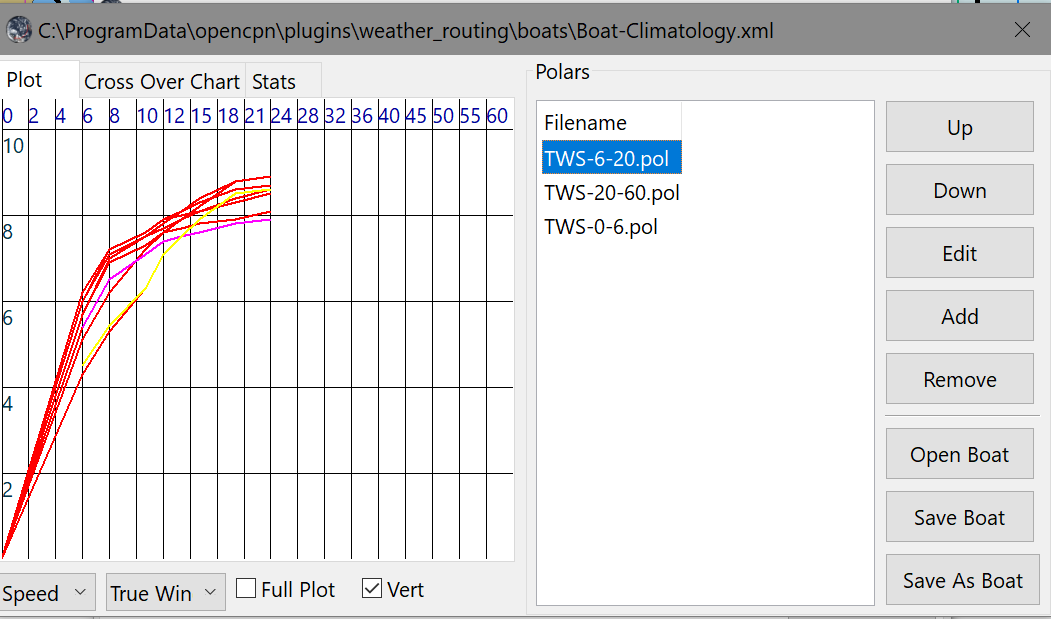
Plot Tab
Shows the highlighted polar file graphically as a familiar polar diagram. Note that the dropdown menus at the bottom provide different useful ways of viewing the boat performance data.
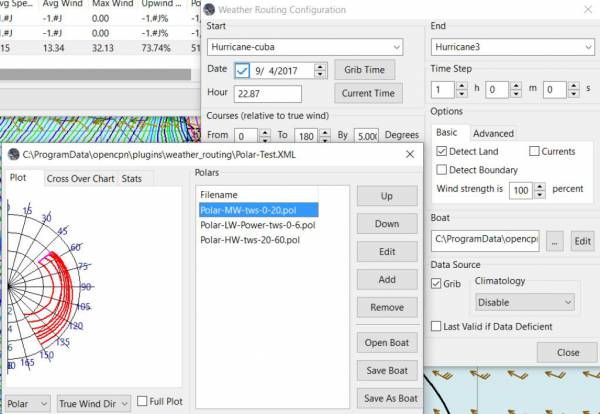
Stats Tab
Shows target speeds.
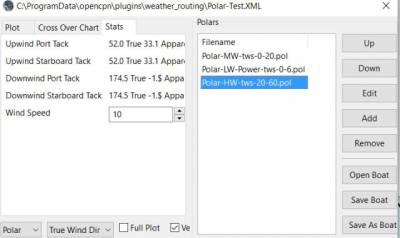
Complete Setting up “Boat” Performance & Polars
-
Weather_routing_pi will use this data to calculate the most favorable route.
-
Later you can find a Boat Polar file that is closer to your boat.
-
Click Save Boat to close the menu and save the [Boat]/Polar-Test.xml file.
-
Then “Close” Weather Routing Configuration Menu.
9. Compute "Configuration" in WeatherRoutingConfiguration.xml Menu
-
In the WR WeatherRoutingConfiguration.xml menu, highlight the Configuration you’ve created and select Compute.
-
Now new isochrones will be created and a weather routing from Boston to Halifax will be “completed”.

10. Messages in Configuration Window
In the Configuration Menu after “Compute”, a message will show to the right of the Configuration.
“Complete” affirms that the computations completed. “Fail” indicates they did not and that some setup parameter may be out of range. The failure messages have been made to be more descriptive to help.
If your polar doesn’t include boat speeds:
-
Above a windspeed that the grib tries to use, it will fail to route.
-
Below a windspeed that the grib tries to use, it will fail to route.
There are many reasons a Computation cannot complete, or fail. The computation is dependent on:
-
Wind Data (grib_pi or climatology_pi) - Start & End data/time of the file, interval downloaded.
-
Boat Polar File - Correct format, with a wind range that matches the grib data.
-
Time Interval Issues - Sometimes a 1/2hr or 1hr interval will yield a better route than 3hr or 3hr. Sometimes that is the difference between “Completion” and “Fail”.
-
Max Diverted Route - Normal setting is 100 degrees, which speeds up calculations, but with longer time intervals, you may have to set this on something like 140-160 degrees to complete the routing, particularly when the Finish is near land with Islands and Peninsulas around.
-
Configuration settings which must be made to be compatible with the data to Complete:
-
Interval Issues - Too long a calculation interval for the distance between start and end.
-
Land Detail - Detect land is checked and the High Resolution GSHHS Shoreline is not installed.
-
Land Interface Issues - Routing near land is complex, if there is a failure at the interface with land zoom in and look at the Isobars. Sometimes they are not calculated for all locations due to the complexity of the land (limited by too many iterations). In that case try making a new Weather Routing Position nearby where there are isobars shown.
-
Max Diverted Course - When “Polar:Fail” or “Polar:No Data” occurs near the “finish” using large Time Intervals (4hr - 24hr). Zoom in and look at the route, isochrones, finish, and land. If the route is almost completed to “Finish” (with land, islands and peninsulas around) try changing Max Diverted Course from 100 degrees to 150 degrees and run it again. It will probably complete.
-
Different Time Intervals - Everything Else is the same.
Beginners should first try a simple route, with starting point and end point, 5 degree steps, and possibly a 3 hour time interval until they see it is working. The time interval depends on the speed of the boat and distance traveled, grib file downloaded.
-
If the Configuration was completing Computation earlier and you changed a setting, check that first.
-
If a Configuration fails, another thing to try is Reset All, and go through the setup sequence above, again.
-
If “Polar:Failed” try increasing or reducing the Weather Routing ConfigurationWind Strength % (50%, 150%) because the Polar File may not have the required winds specified. The grib file may have periods of very high winds or very low winds which are not covered by the polar diagram wind range.
-
Then try using different data, either change the grib start date, moving it forward, or try using only Climatology Data, or change the Polar File to something else, or add multiple polar files, just to get the Configuration working.
11. Configuration - Edit
Provides setup flexibility for various factors:
-
Start location, date and time. End location.
-
Step duration for isochrones in hours and minutes (12 hours for long routes, 1 hour for shorter)
-
For Time Step I generally start larger and once things are working, go smaller, the distance governs what the tme step is.
-
Divide the time expected to sail the course into 10 and use that number for the Time Step. Then adjust as needed.
-
Degree Steps (5 degree steps is faster than 1 degree steps). Generally leave Courses (relative to true wind) alone, From 0 to 180 by 5 degrees is fine.
-
Boat Performance based on editing boat specifications or based on a polar data file.
-
Set constraints on various factors such as max wind, swell, waves, latitude, max diverted course etc…
-
Start Grib_pi and/or Climatology_pi
-
Set Grib_pi to the date and time you want to use.
-
Then go to the Weather_routing Config menu and pick “Grib Time”
-
Set options like detect land, currents, inverted regiions, anchoring.
-
Routes can be Edited (created, selected, renamed, reset and exported.)
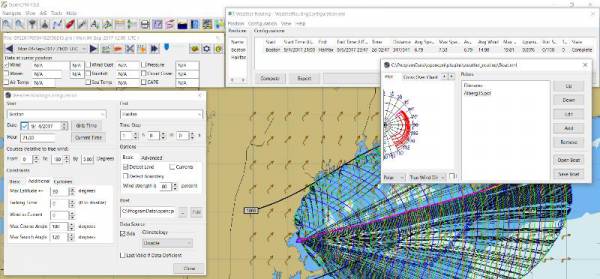
Configuration and Edit Boat.xml,title="WR Configuration and Edit Boat.xml",width=600]]
12. View
13. Use with Grib_pi
Boat position (round circle) is when stepping through the grib file (assuming you use a grib file and not climatology of course).
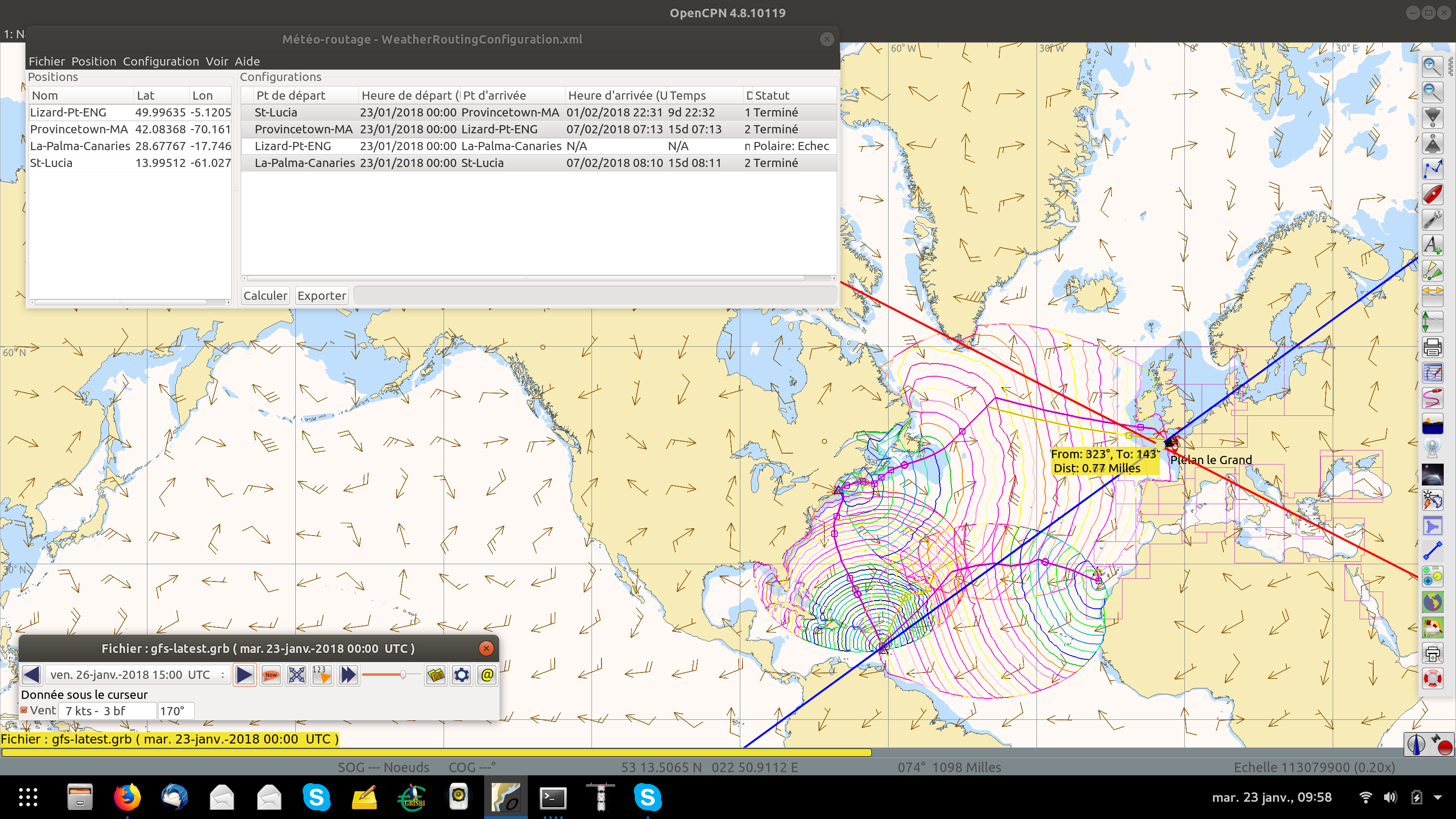
Moreover, if multiple routes are computed and shown (selected), when stepping through the grib the boat position is shown simultaneously on each route.
that: when you step through the grib you will see the boat position at that current grib time (not “the multipier of the two time intervals”). This can be right on an isochrone or between two isochrones (if grib interval is smaller than wxrte time interval).
15. Use with Route Manager
The Route Manager can be used for listing the weather route. Right click a weather route and pick “Properties”. Also a Weather Routing can be Exported to a gpx file or saved to a Route in Route Manager.
Two Grib Files (Wind + Current)
Weather Routing will use two grib files that are loaded by Grib_pi. This is useful when you have downloaded a GFS Wind and Pressure Grib, and an RTOFS Current Grib of similar time period and resolution. First Load two Grib Files Concurrently (Wind + Current) in Grib_pi. Then in WR Configuration check the Currents box.
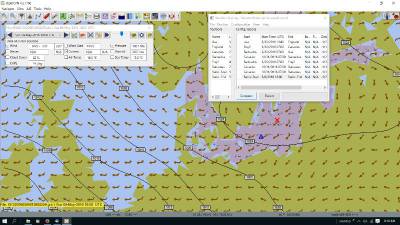
In this Baltic Sea example there is an underlying current file with black arrows and the area of the grib is shown in light read. The wind
pressure grib is shown with brown arrows with feathers.
Ocpn_Draw_pi (Boundary with guid)
Create Boundaries recognized by Weather_Routing_pi. Useful for guiding routing.
Red hatched Boundary along the Nova Scotia coast was created in Ocpn_Draw and used in weather_routing, to prevent routing in that area.
Red hatched Boundary created with Ocpn_Draw and used in Weather Routing Configuration > Options > Basic Tab > Check “Detect Boundary”
FAQ
This section is meant to deal with various questions that might arise
when using the pi. Example: (Why) Can(‘t) I? Answer:
Why does the "Computation" of a "Configuration" always fail with the message "Polar:Fail"? It is very frustrating.
-
See: CF Thread Polar Fail
What can I do about "Polar:Fail"?
-
Add other polars to the boat file to cover those wind speeds.
-
Increase or Decrease the Interval, try 1 hr to 8hr. This does make a difference, and sometimes an alternate optimal route will appear.
-
Reduce Wind to 50% or 25%.
-
Increase Wind to 110% or 125%.
-
Use Boat.XML or Boat-Test.xml with TWS 0-60 knots.(original file, unchanged)
-
Use a different set of Polars.
-
Find the high or low wind area and times, then change the route accordingly.
-
Try a different grib file from another time with in the same area.
-
Zoom into where it fails and look. Near land can cause problems.
-
Try making a slightly new Destination point if it fails just short.
I can’t seem to get this to complete a weather routing, what is wrong?
-
Undo the most recent changes you have made if you had it was working recently.
-
When this happens go back to basics, Reset to default settings. See the CF Post
about this and refer to the default list in this manual above. Or download the Weather_Routing_Setup above, install it again and start over.
Routings, with climatology only, seem to be missing voyage data, such as duration, time of start and finish—If we are using a specific date and time for the start, why is this happening?
It is most likely that the routing did not reach the destination. -Understand that the routing ends if destination is inside two isochrones, which is likely what you have, but remember between these two isochrones the boat can only move in straight lines and if there’s land in the way, the destination could be unreachable. Islands and Harbors are very prone to this kind of issue.
Try a new destination (or start) well outside of the harbor. This issue occurs at both the start and the finish when the routing is tends to be near land with islands, harbors and complex shorelines, or try shortening the interval.
Why doesn’t synchronize position on route, display with grib display? No red circle.
Try uninstalling the weather_routing plugin and removing all files and configuration from the system as outlined in the manual then re-install and make a new configuration. Now you should see a red circle moving along the route as you step thru the Grib file.
Edit Boat > Plot Tab What is the difference between the faint yellow line and the magenta line?
-
These are the optimum upwind and downwind lines for best velocity made good. The colors show up best with the left dropdown set on “Speed” rather than “Plot”
View > Route Position > Boat Speed
-
Boat Speed is shown as SOG and SOW when they are different. If they are the same, only one value is shown.
Weather_Routing Time Intervals and Grib Data Time Intervals
When you step through the grib you will see the boat position at that current grib time. This can be right on an isochrone or between two isochrones (if grib interval is smaller than wxrte time interval).
Grib data Time Interval: Available in 3,6 and 12 hour intervals. Weather_Routing Time Interval: Often set to a smaller interval, say 3 or 1 hour intervals. But sometimes to complete to the destination the interval has to be set considerably smaller, say 10 minutes. Weather_routing will then interpolate the Grib file interval down to 10 minutes. When you try to step through the grib file to understand the conditions on the routing, you will jump across the interpolated isochrones. This is determined by the weatherrouting time interval.
For example: From the WeatherRoutingConfiguration results the arrival time is 21:33, for a departure at 12:00. This means a duration of 9 hours, or three grib intervals of 3 hours. Consistent with the 3 steps in grib controller (3 hour time intervals). If you have weather_routing time interval set to 10 minutes, the boat will skip over 18 isochrones for each step of the grib controller.
Supplemental Hardware and Software
-
Polar tools - Polar_pi, Polauto (Windows) (See above)
-
Voyage Recordings to create polars: Use Opencpn VDR_pi RPI3 or Yacht Devices Voyage Recorder
-
Yacht Devices using Excel:
-
Additional Polars Qtvlm Polars
We contributed so there may be duplicates.
Warnings
Warning about Data
Weather_routing is only as good as the data provided by the Grib plugin and the Climatology plugin.
-
Grib plugin: Depends on recent download grib files from Noaa and other sources. Downloaded Grib predicitions can change significantly over several days. The longer the grib prediction is, the less reliable the grib can be.
-
Climatology plugin: Can be used for analyzing long crusing routes through various seasons and constraints, but does not take into account the current weather conditions which often vary significantly from the 30 year average, especially outside of prevailing wind areas.
-
These planning tools may be helpful, but should be taken with a healthy “grain of salt” as any good sailor (who looks out to the horizon) should know.
Warning about Weather Routes
The weather routes created may not consider or “see” normal navigation considerations and issues, therefore every route should be checked very carefully for navigation markers, shallow depths, bad currents, rocks, land and other obstacles and hazards.
Developer Notes regarding Packaging for Configuration of the Installation files
Stelian wrote:
In fact, the paths in WeatherRoutingConfig.xml and the boat XML files need to be there, because they tell the plugin where to find the corresponding boat/polar files. And since there might be several boat or polar names with the same name (but located in different folders), the paths need to tell which one is to be used.
However, there is one exception to this: at the packaging time, we don’t know where the files will be installed - we know we want to put these in the user directory (ProgramData), but this path is dynamic, it depends on the user name (in case of multiuser systems). For example, on Linux, it might be /home/stelian/.opencpn/plugins/… or /home/rick!
So what we’ve done is to change the code to allow the config file to use name without the path. The plugin, when it tries to open the file and if there is no path before, will automatically append the user directory path. This is why the xml files containing the default configuration need to have only the filenames and not the paths inside.
Moreover, the files can contain the path to the contours. This path, once again, is dependent on the user. So we’ve just removed the CrossOverContours from the boat xml files, and made sure that the plugin will regenerate the contours upon start.
For the date problems, well, we simply noticed in the XML file that the dates were in mm/dd/yy format, so I’ve just modified them to yyyy-mm-dd, (if you had saved the files using the current version of the plugin this should have been done automatically).
There was an hour issue too, the file had 09:00 (local time I suppose), I put 00:00:00 instead, I don’t think it matters much anyway for such long routes.
I also renamed a boat.XML file to .xml (notice case), it’s more standard that way (I know that windows doesn’t care much, but on the other systems the conventions are quite strong).
Notes
New dialog to display which sail plan is at the cursor in View→Cursor Position. Alternately it might be interesting to have a display option to color the route map the same as the cross-over chart. There is a box on the route to show each sail change.
Author
Weather_routing_pi is written by Sean D`Epagnier programmer excellente. Sean’s Website